The three tests used were infrared spectroscopy Bromine chemical test and Bayers chemical test. Lab 4 - Dehydration Of Alcohols-Gas Chromatography - Lab Report Gas Chromatography - The Laboratory Report is among the lots of resources available to you on the Internet for a broad range of education details associated to your lab work.
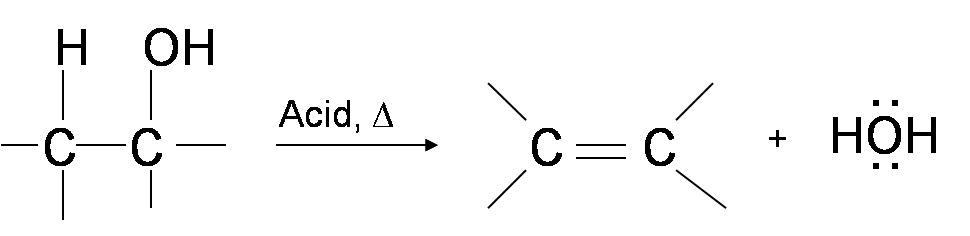
14 4 Dehydration Reactions Of Alcohols Chemistry Libretexts
This chart was upload at February 13 2021 upload by Admin in Lab Report Sample.
Dehydration of alcohol examples. It is an example of an elimination reaction. Once the fraction has been collected it must then be dried. Dehydration Reaction Examples.
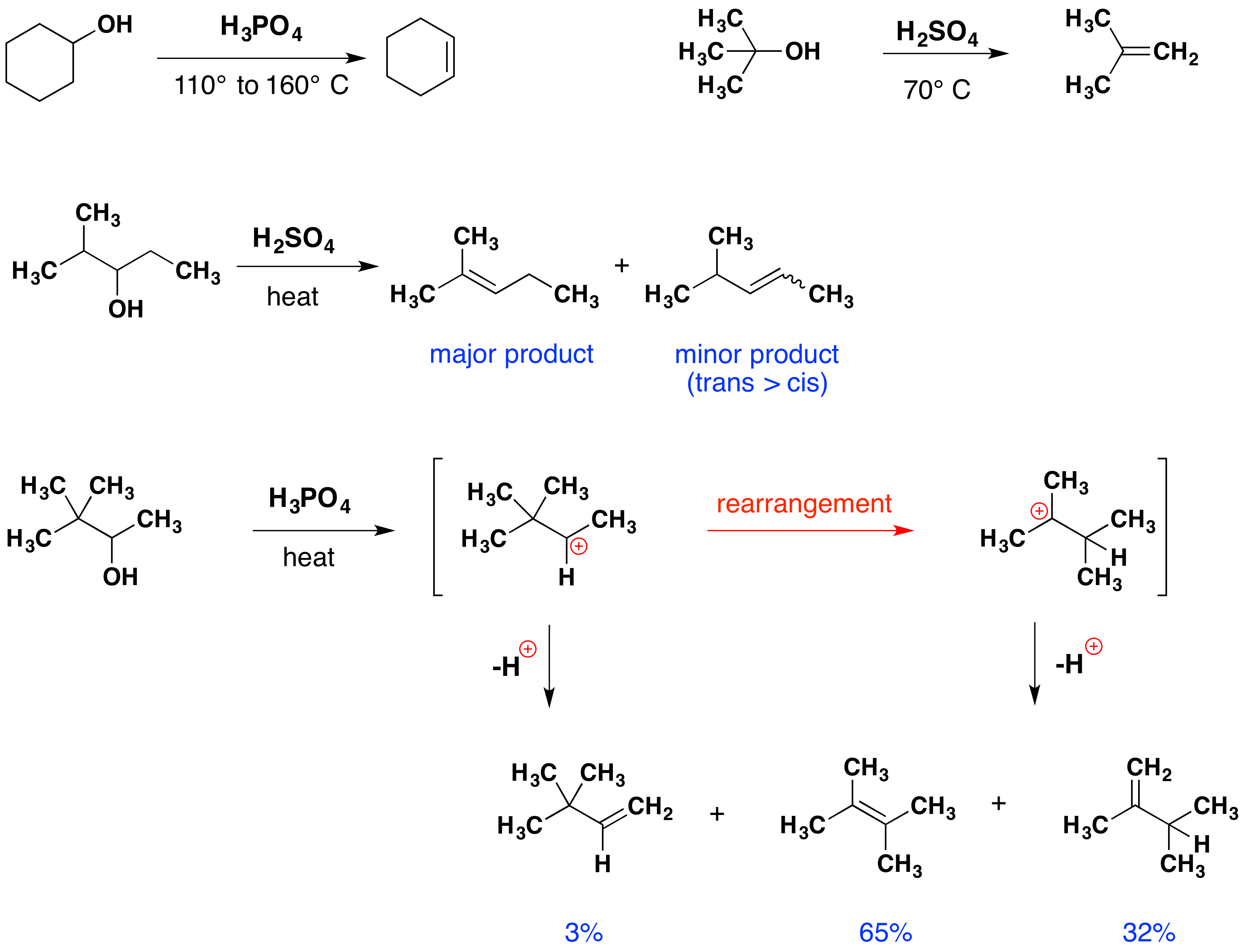
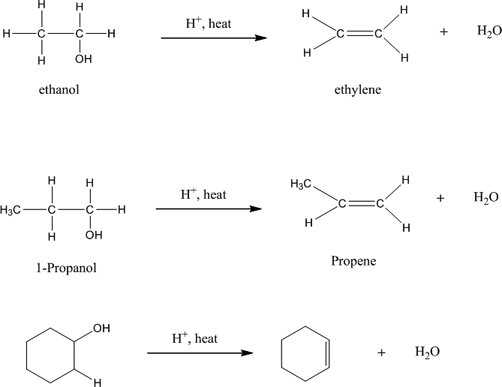
Dehydration of Secondary Alcohols Secondary alcohols require more concentrated acid solutions and higher temperature. The formation of a chemical known as the carbo cation intermediate. For example cyclohexanol is dehydrated to form cyclohexene using concentrated sulfuric acid at 160180 C.
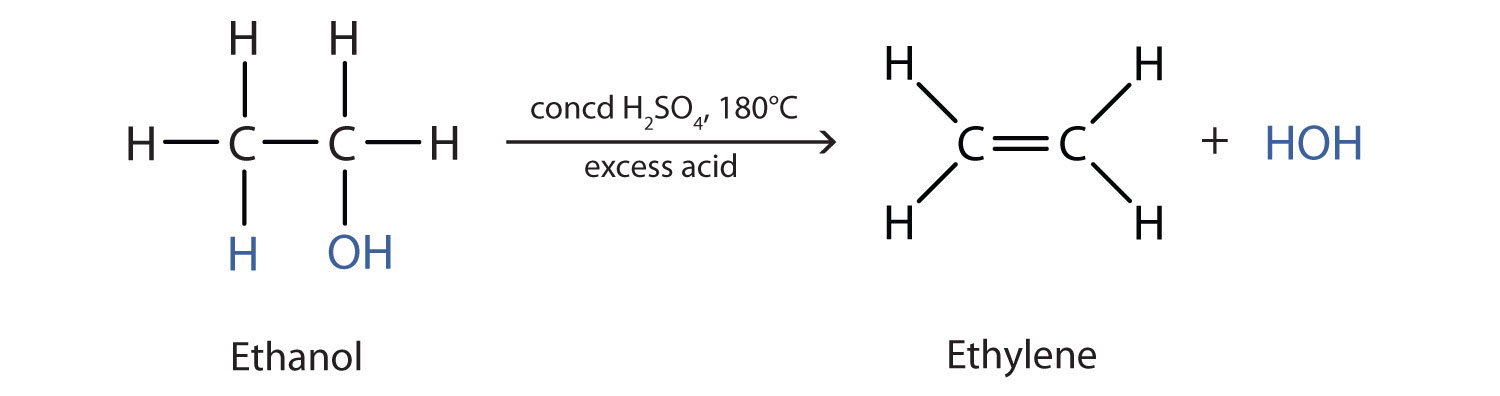
At 180C concentrated sulfuric acid will dehydrate ethanol to produce ethene CH 2 CH 2 ethylene and water. The dehydration of more complicated alcohols. Secondary alcohols are oxidized to form ketones.
Reactions that produce acid anhydrides are dehydration reactions. Primary alcohols are oxidized to form aldehydes. Alcohol dehydration is an example of an elimination reaction which is quite the opposite of substitution reaction and addition reaction.
Tertiary alcohols are not readily oxidized. It is important that you understand it so that you can. What is Dehydration of Alcohols.
The dried distillate is finally tested to determine whether or not it has been dehydrated. Dehydration of Alcohols Abstract The dehydration of cyclohexanol to cyclohexene can be done through fractional distillation. You have to be wary with more complicated alcohols in case there is the possibility of more than one alkene being formed.
Examples of these and related reactions are given in the following figure. When heated with strong acids catalysts alcohols typically undergo a 12-elimination reactions to generate an alkene and water. These reactions are known as dehydrogenation or dehydration of alcohols.
Its rate varies for primary secondary and tertiary alcohols. AlcoholsandPHenols DehydrationOfAlcohols ChemistrybySambarkarSir MechanismofDehydration Elimination Reaction AlcoholtoAlkene. This variation of rate can be attributed to the stability of carbocation generated.
Alcohols react with strong acids due to lone pairs on oxygen to form oxonium salts in this case protonated ethanol. The products of the dehydration of a primary alkanol are water and an alk-1-ene 1-alkene. Butan-2-ol is just an example to illustrate the problems.
You need to always have access to the most recent reports and. Dehydration of alcohols using aluminium oxide as catalyst The dehydration of ethanol to give ethene This is a simple way of making gaseous alkenes like ethene. Alcohol dehydration generally requires the cleavage of a C-O bond and the loss of a proton from the beta place.
Alcohol upon reaction with protic acids tends to lose a molecule of water to form alkenes. This page a simple duplicate of a page in the section on alkenes looks at the dehydration of alcohols in the lab to make alkenes - for example dehydrating ethanol to make ethene. Dehydration of Ethanol to Produce Ethene ethylene Ethanol CH 3 -CH 2 OH ethyl alcohol is a primary alcohol.
Alcohols can be dehydrated to form either alkenes higher temperature excess acid or ethers lower temperature excess alcohol. Elimination reaction d internal substitution reaction. The dehydration of alcohol is an example of a Bimolecular elimination reaction.
For example acetic acid CH 3 COOH forms acetic anhydride CH 3 CO 2 O and water by the dehydration reaction 2 CH 3 COOH CH 3 CO 2 O H 2 O Dehydration reactions are also involved in the production of many polymers. The first equation shows the dehydration of a 3º-alcohol. Butan-2-ol is a good example of this with no less than three different alkenes being formed when it is dehydrated.
An elimination reaction is a type of reaction wherein 2 groups or 2 atoms on neighboring carbon atoms are eliminated or removed from a molecule which leaves multiple bonds between the carbon atoms. The predominance of the non-Zaitsev product less substituted double bond is presumed due to steric hindrance of the methylene group hydrogen atoms which interferes with the approach of base at that site. The reaction still goes by E1 mechanism and the rate depends on the stability of the secondary carbocation.
One of the most common dehydration reactions involves the conversion of an alcohol to an alkene as shown here for the dehydration of ethanol to. The second example shows two elimination procedures applied to. Formation of alkene mechanism The mechanism of formation of alkene by dehydration can be understood by using the example of ethanol CH 3 CH 2 OH.
Dehydrogenation is an important process in petroleum chemistry because it converts inert alkanes into olefins and aromatic compounds which serve as starting points for other functional groups. Also known as dehydration since it involves the removal of a molecule of water.
Discuss The Mechanism Of The Following Reactions A Dehydration Of Alcohols To Form Alkenes

Alcohol Dehydration By E1 And E2 Elimination With Practice Problems Chemistry Steps
Definition Of Chemical Reactions Of Alcohols Chegg Com
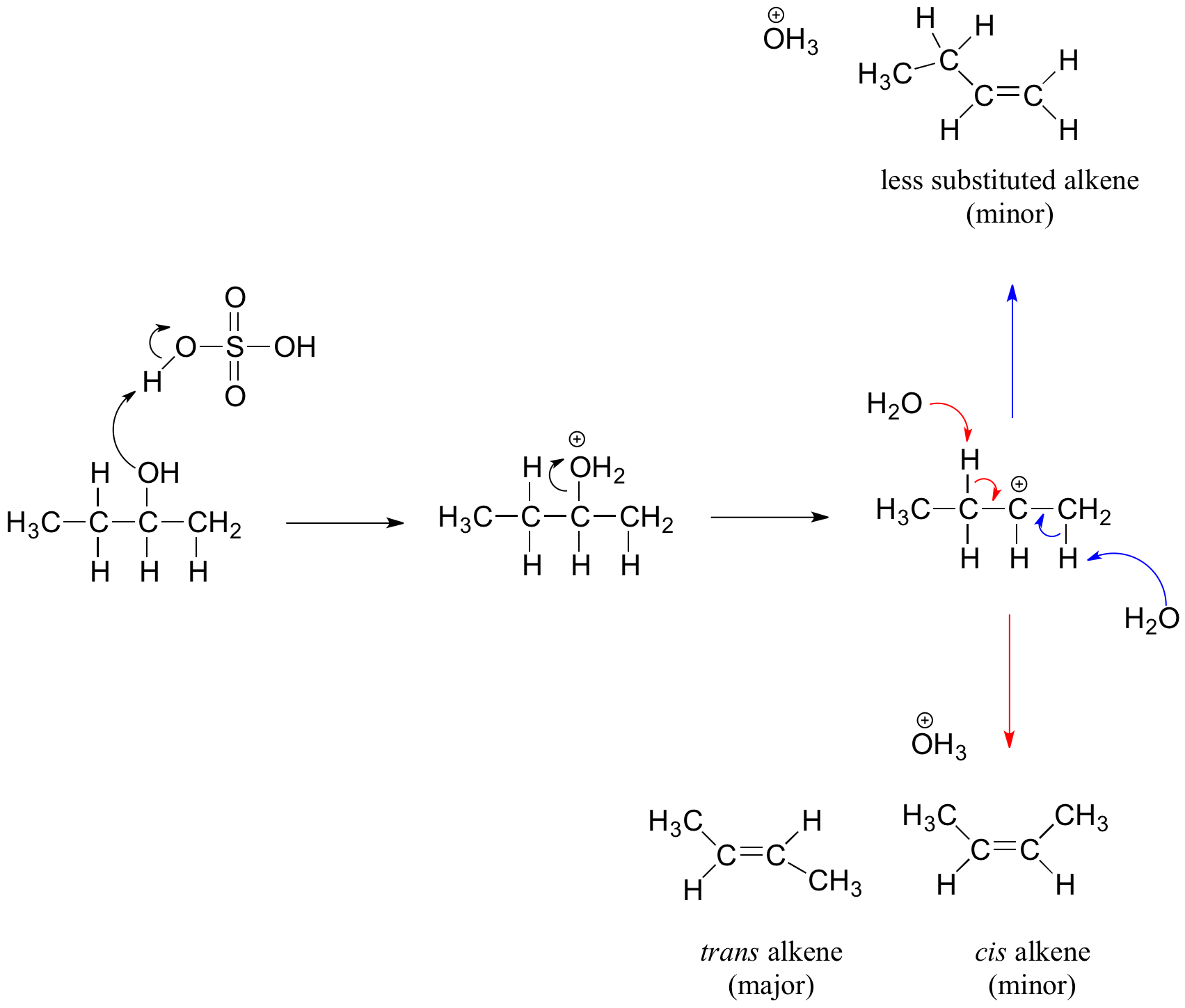
14 4 Dehydration Reactions Of Alcohols Chemistry Libretexts
Dehydration Of Ethanol To Give Ethene

Dehydration Of Alcohol Rearrangements Mechanism Chemistry Alcohol Alcohol Dehydration

Alcohol Reactions Of Alcohols Britannica

Alcohol Dehydration By E1 And E2 Elimination With Practice Problems Chemistry Steps

10 8 1 Dehydration Of Alcohols Chemistry Libretexts

Dehydrogenation Dehydration Of Alcohols Mechanism Examples With Videos Faqs

14 4 Dehydration Reactions Of Alcohols Chemistry Libretexts
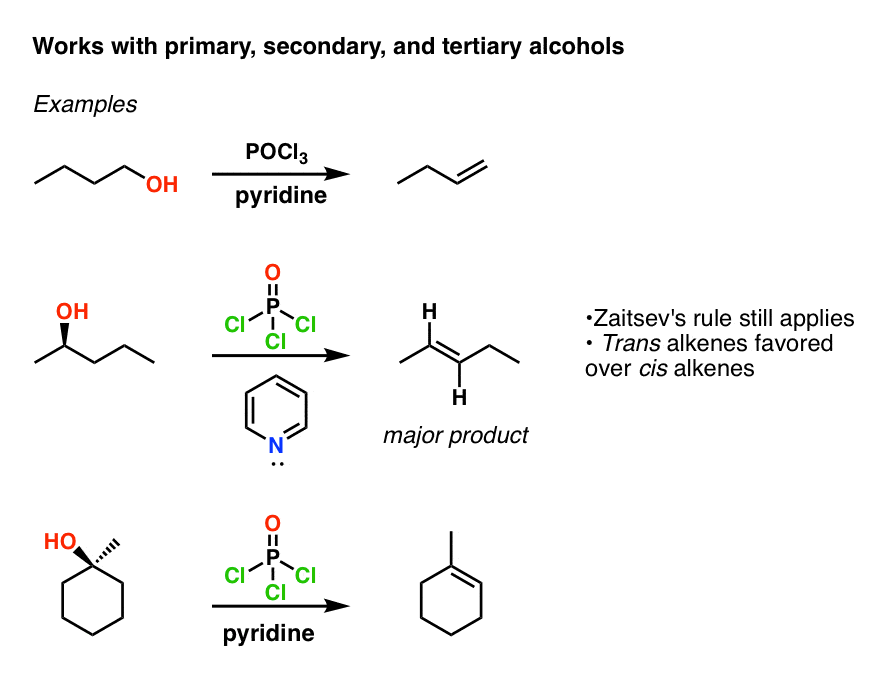
Elimination Of Alcohols To Alkenes With Pocl3 And Pyridine

How Does Dehydration Of An Alcohol Occur In Alkaline Medium Chemistry Stack Exchange