Iii The transmission of virus diseases is a classical example of dissemination of plant diseases through insects. DISEASE TRANSMISSION 3.
DYNAMICS OF DISEASE TRANSMISSION SOURCE MODES OR I.
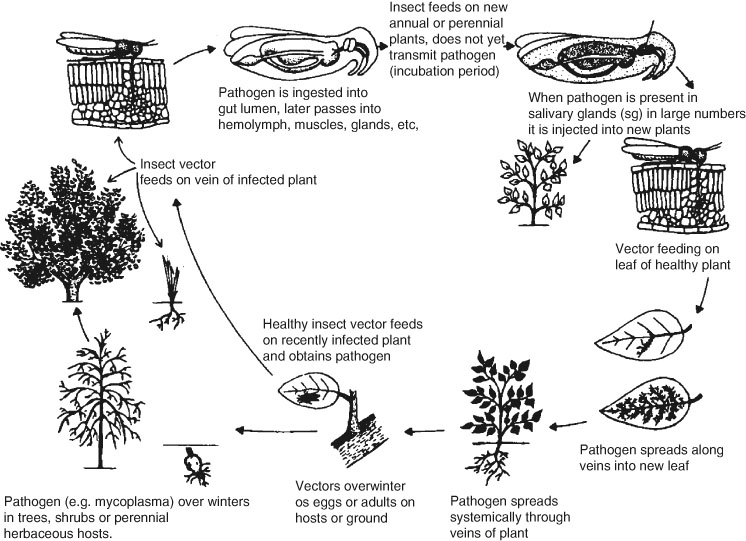
Mode of transmission of plant diseases. The following points highlight the eight chief methods used for the transmission of plant viruses. An infectious agent may be transmitted from its natural reservoir to a susceptible host in different ways. Transmitted by insects either accidentally several fungi and bacteria or by a specific insect vector on which the pathogenic organism some fungi some bacteria some nematodes all protozoa causing disease in plants and many viruses depends on for transmission from one plant to another and on which some pathogens depend on for survival.
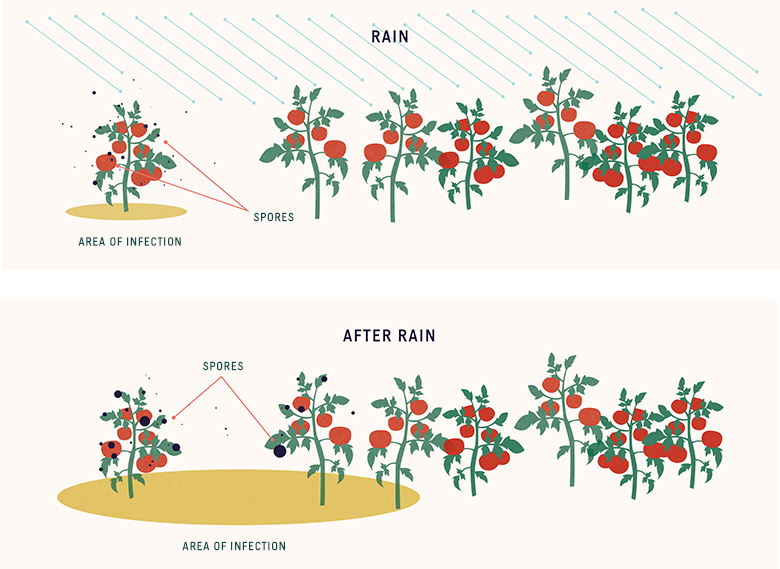
Natural grafting and transmission are possible by root grafts and with parasitic dodder Cuscuta species. Many plant pathogens are transmitted by hemipteran insects in a circulative manner meaning that the pathogen is ingested and moves throughout the body of the insect prior to transmission to a new host plant. - Fungal spores produced externally on host surfaces are most easily carried by wind currents and this is the most dangerous mode of transmission of plant pathogenic fungi like those causing powdery and downy mildews leaf spots blasts blights and rust diseases.
Examples are hookworm and legionnaires disease. The black stem rust disease of wheat in India perpetuates on wild grasses in the Nilgiri hills in the south India from where. DEFINITION Disease Transmission is the passing of a communicable disease from an infected host individual or group to a conspecific individual or group regardless of whether the other individual was previously infected.
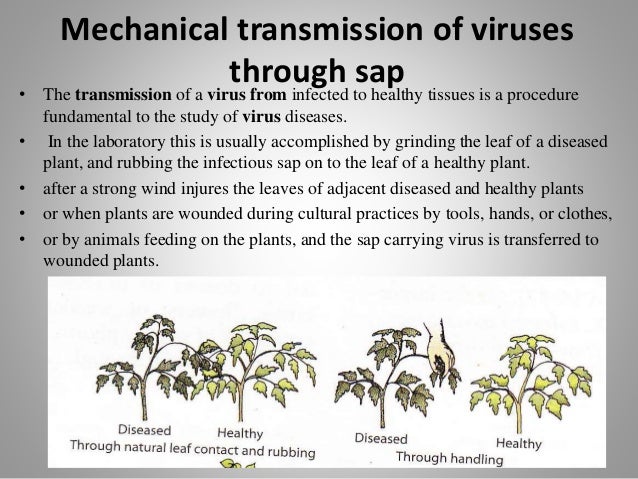
Plant disease an impairment of the normal state of a plant that interrrupts or modifies its vital functions. Mite-borne plant viruses may cause severe or even crippling losses to many annual and perennial crops in the tropics and semi-tropics which provide ideal conditions for the perpetuation of viruses and their vectors. Recognize a virus as cause of the disease if transmitted from infected to healthy plant How virus spread in field help in its control Establish biological relationship of interaction between virus and its vector Mechanical transmission is very important for lab.
Cajani acquired PPSMV after a minimum acquisition access period AAP of 15 min and. For eg if an open wound comes in contact with the blood of a Hepatitis B infected patient the wounded person might contract the disease. Transmission by Vegetative Propagation 3.
Transmission by Cuscuta 5. Most plant viruses depend on vectors for their survival and spread. Direct Transmission This occurs when the pathogen is transmitted directly from an infected person.
Vegetative propagation often spreads plant viruses. Cajani was up to 53 but was 100 when 5 mites per plant were used. More specifically transmission occurs when the agent leaves its reservoir or host through a portal of exit is conveyed by some mode of transmission and enters through an appropriate portal of entry to infect a susceptible host.
The transmission efficiency of single A. Insects like leaf-hoppers and aphids feed on virus infected leaves and they go and feed on leaves of disease-free hosts and thereby spread infection behaving as. Plant diseases can be classified as infectious or noninfectious depending on the causative agent.
Learn more about the importance transmission diagnosis and control of plant diseases. Transmission by Mechanical Means 4. Transmission by Fungi 8.
Airborne transmission refers to diseases that can remain in the air like oxygen and water remain in the air and that can survive for long enough periods of time that they can find a new host. Vertical transmission occurs when a plant gets it from its parent plant. Seed Transmission of Virus 2.
They may come in contact with people who can cause diseases. Either through asexual propagation cuttings or in sexual reproduction via infected. Airborne particles are then inhaled by a new host who will then either become sick and show symptoms or become a carrier of the disease.
There are two different modes of transmission of diseases. The knowledge of virus transmission is important to. Several infectious modes of disease transmission are available in water plants and soil.
All viruses that spread within their host tissues systemically can be transmitted by grafting branches or buds from diseased plants on healthy plants. OF _ SUSCEPTIBLE.
Transmission Of Plant Diseases By Insects Springerlink

Transmission Mechanisms Shape Pathogen Effects On Host Vector Interactions Evidence From Plant Viruses Mauck 2012 Functional Ecology Wiley Online Library

How Do Diseases Spread Between Plants

Insect Vector Mediated Transmission Of Plant Viruses Sciencedirect
How Do Diseases Spread Between Plants
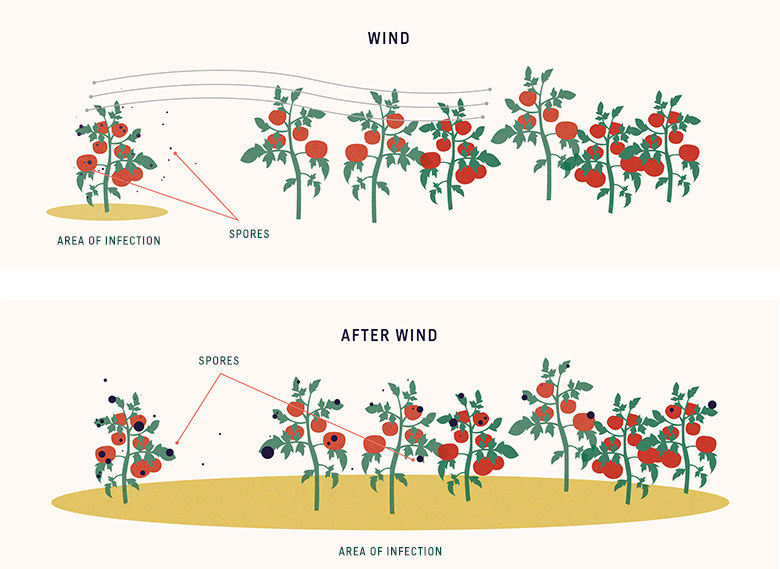
How Do Diseases Spread Between Plants
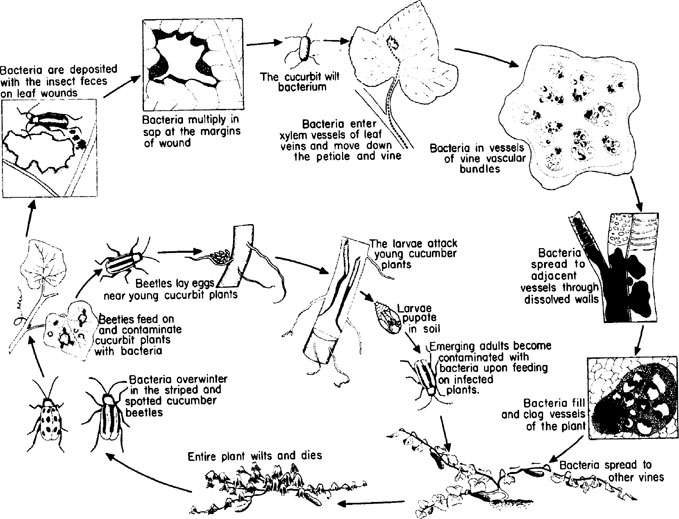
Transmission Of Plant Diseases By Insects Springerlink
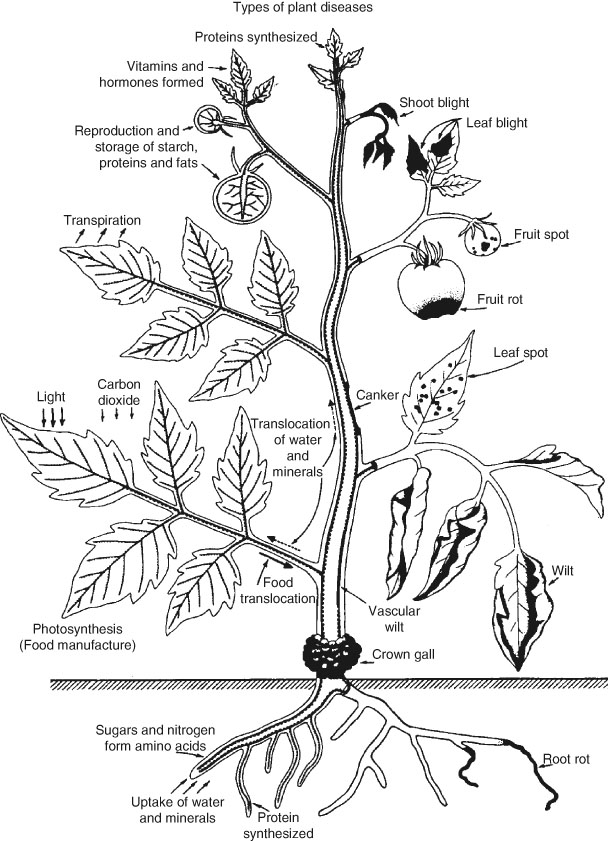
Transmission Of Plant Diseases By Insects Springerlink

Transmission Of Plant Viruses Virology The Biology Notes

How Do Diseases Spread Between Plants
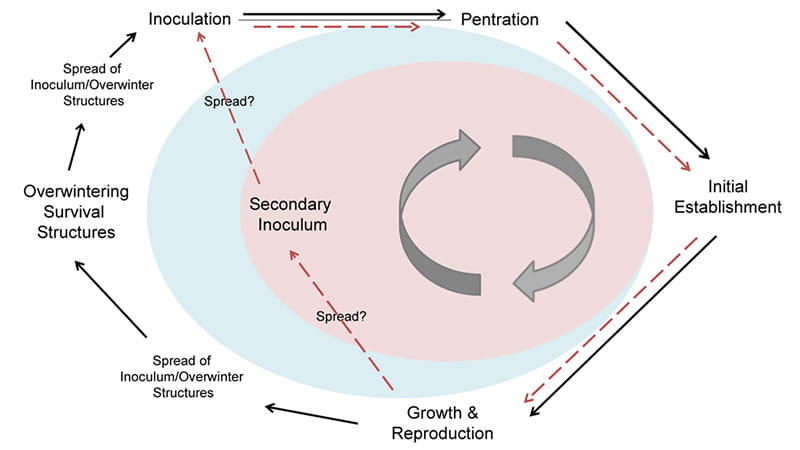
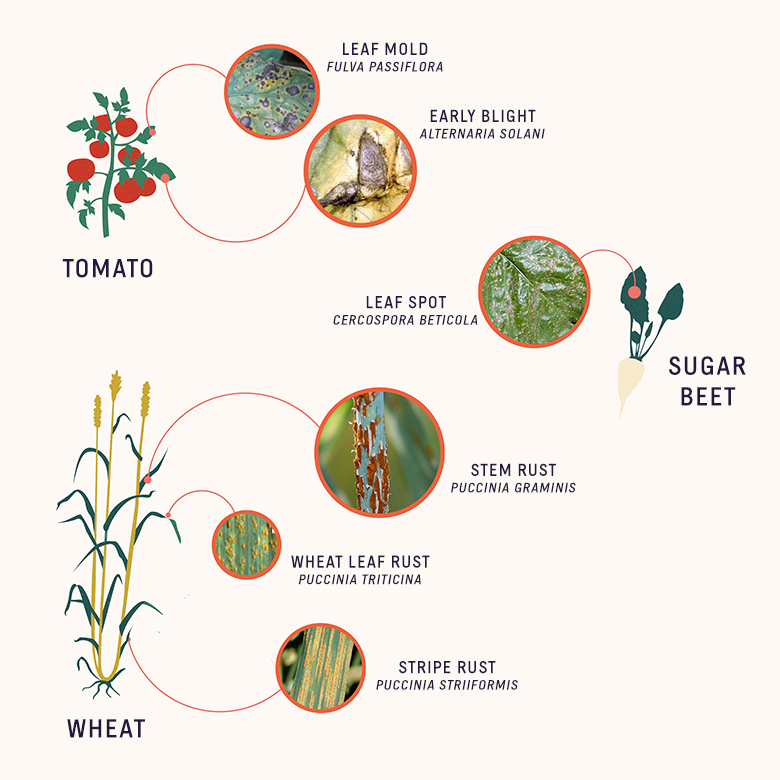
Plant Disease Pathogens And Cycles Cropwatch
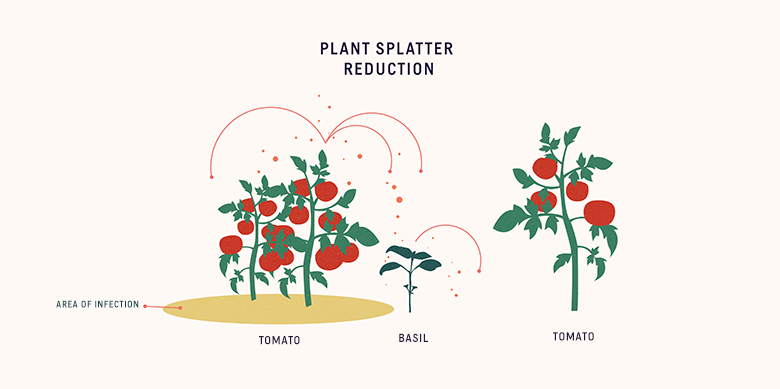
How Do Diseases Spread Between Plants
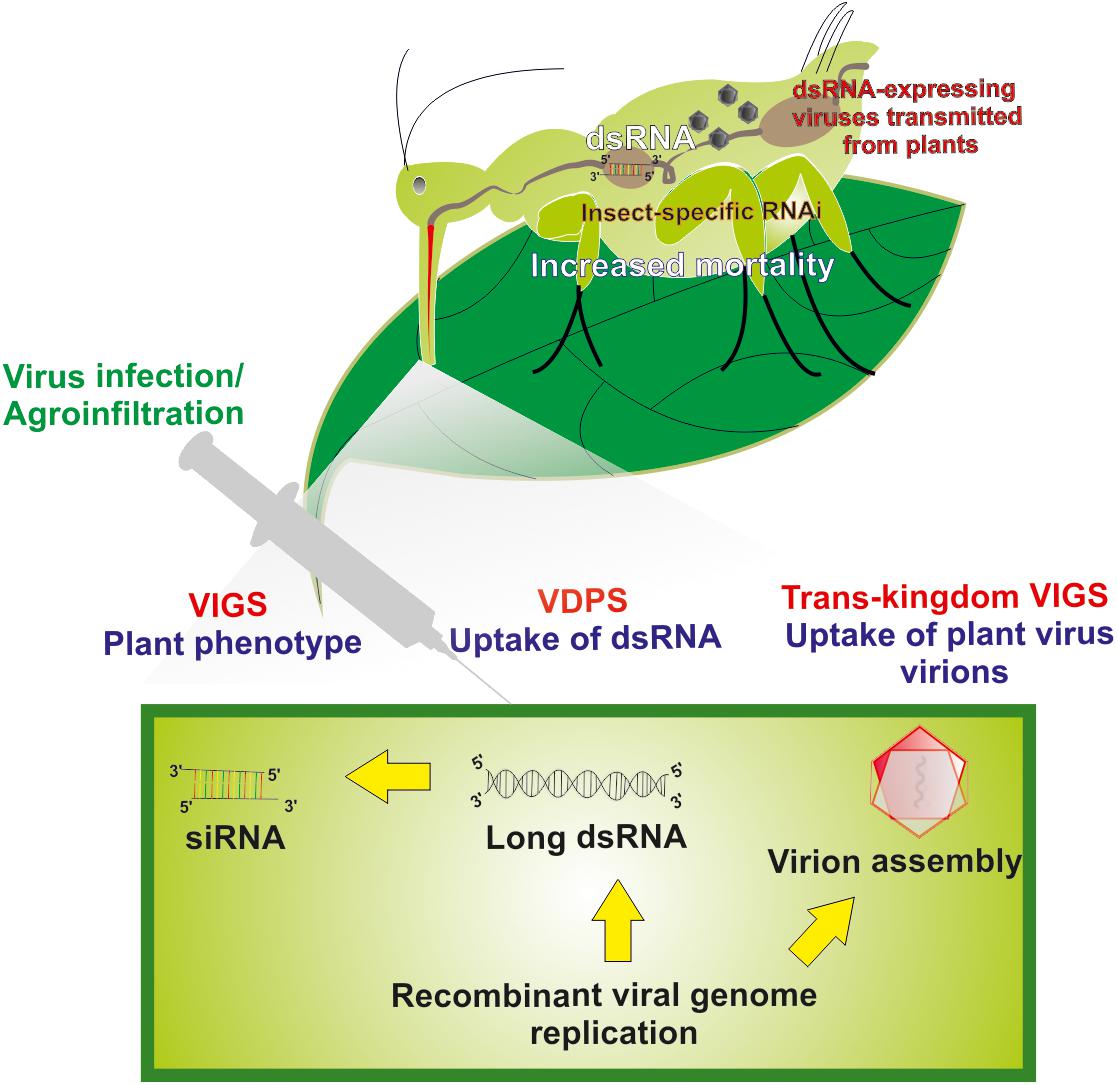
Frontiers The Use Of Engineered Plant Viruses In A Trans Kingdom Silencing Strategy Against Their Insect Vectors Plant Science