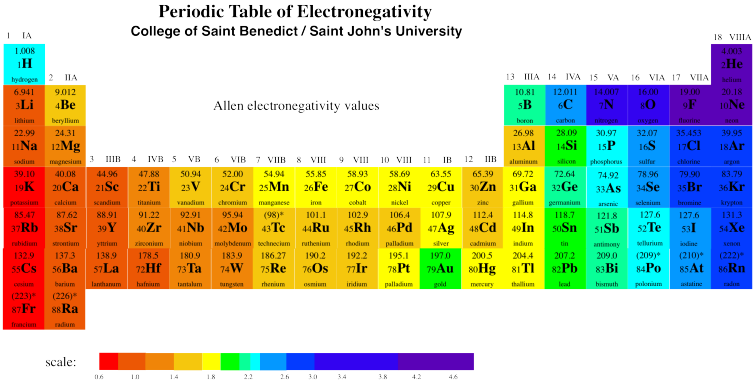
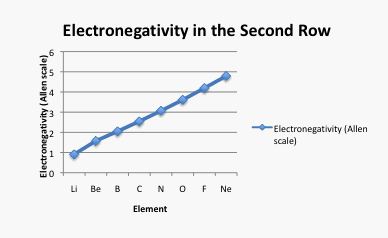
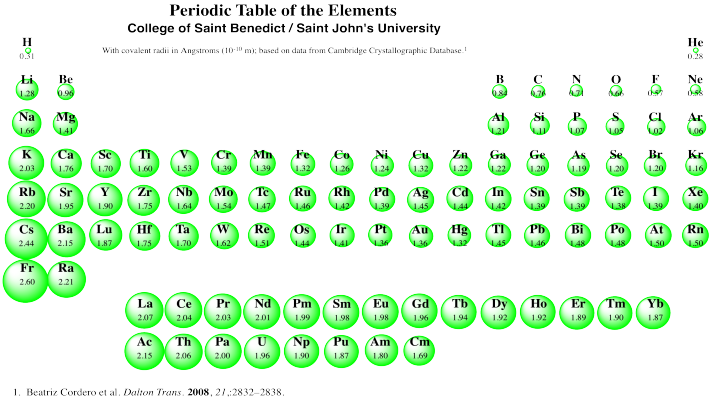
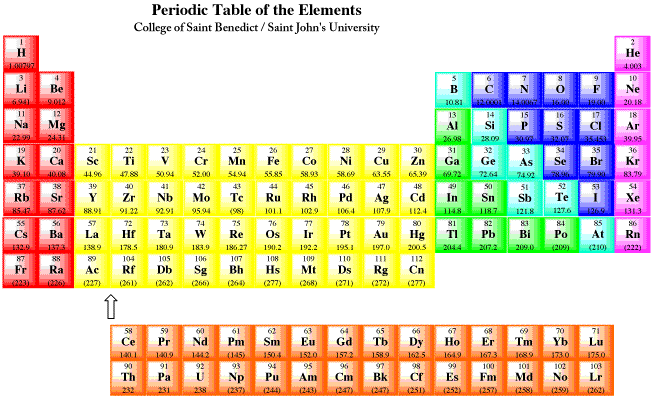
The number of protons and neutrons. The reverse is true of elimination reactions iethe number of σ-bonds in the substrate decreases and new π-bonds are often formedSubstitution reactions as the name implies are characterized by replacement of an atom or group Y by another atom or group Z.

Pdf Electron Configuration And Reactivity Of Chemical Elements
The valence electrons are the outermost electrons in an atom.

The chemical reactivity of an atom is dependent on. The larger the atomic radius electrons further from the nucleus the less is the reactivity of an element. D the number of protons and neutrons. However clear examples of conformation-dependent bimolecular chemical reactions are lacking.
Reactivity Trend in the Periodic Table. As per charge distribution on 12-dithiolylium cations the C 3 or C 5 site is least electron dense and prone to preferential nucleophilic and free radical attack but is quite resistant to electrophiles. Chemical reactions depend on the movement of electrons.
Which of the following is the chemical reactivity of an atom dependent on. Atom Chemical Reactivity Reactivity is dependent on how likely it is that a chemical change can take place. C the number of electrons in the outermost shell.
The 3D space where an electron is found 90 of the time part of the electron shell no more than 2 electrons can occupy a. An atom with octet configuration does not participate in chemical reactions and is known as chemically inert. 28 Nov 2020.
Nuclear charge - the more protons there are in the nucleus of an atom the greater the attraction between the nucleus and the outer shell electrons. They are closest to the surface of an atom. Whether matter can undergo chemical reactions with other substances will depend on the.
The chemical reactivity of an atom is dependent on A. The chemical reactivity of an element is dependent on A the number of protons. From atomic number we can get valence electrons that determines the chemical properties of it.
Electrons if the outer most electron cell what the chemical behavior of the cell is most dependent on. The number of electrons in the inner shell. Conformation dictates many physical and chemical properties of molecules.
Answer to The chemical reactivity of an atom is dependent on A the number of protons B the arrangement of neutrons C the number of electrons in the outer. The number of protons and neutrons. Increasing temperature increases the energy available for a chemical reaction usually making it more likely.
The arrangement of neutrons. The reaction surprisingly leads to peroxyformic acid only from the ground-state trans conformer of formic acid and it results in the hydrogen-bonded complex for the higher-energy cis conformer. The chemical properties of an atom depend upon the atomic number.
The importance of conformation in the selectivity and function of biologically active molecules is widely accepted. Atoms with similar electron configurations have similar properties. Here we consider a case of formic acid HCOOH that is a valuable model system containing the COOH.
The chemical activity of an atom is dependent on the number of valence electrons. We have found a strong case of conformation-dependent reaction between formic acid and atomic oxygen obtained in cryogenic matrices. One atom may donate electrons to another atoms.
The last electron shell of an atom. The chemical reactivity of the 12-dithiolylium cation depends upon the charge distribution in the ground state. Atomic radius - the distance between the outer shell electons and the nucleus.
The number of protons. The chemical reactivity of an atom is dependent on its valence electrons. The number of electrons in the outer shell.
E the number of electrons in the inner shell. In a reaction one atom may accept electrons from another atom. The number of electrons in the inner shell.
The arrangement of neutrons. Reactivity is dependent upon temperature. Another definition of reactivity is that it is the scientific study of chemical reactions and their kinetics.
In an addition reaction the number of σ-bonds in the substrate molecule increases usually at the expense of one or more π-bonds. B the arrangement of neutrons.

Chapter 2 The Chemical Context Of Life Reminder
What Determines Stability Or Reactivity Of An Atom

Unit1 Seguin 8th Grade Science

Solved 1s What A Mumber Does The Reactivity Of An Atom D Chegg Com

Elements Compounds Bonds Ppt Download

Bonding Introduction For Science 10 Chemical Reactivity The Reactivity Of An Element Depends On The Number Of Valence Electrons If The Outer Shell Of Ppt Download

Reactivity Of Elements Of The Periodic Table

Elements Compounds Bonds Ppt Download

Forming Chemical Bonds Ppt Download
Solved The Chemical Reactivity Of An Atom Is Dependent On Chegg Com