Particularly in copper but in other metals as well the thermal conductivity is a strong function of the purity and the condition of the metal. You can create a new function using the Function Definition dialog box.
Thermal Properties Of Graphene From Physics To Applications Chapter 6 2d Materials
AZIZOV3 1Azerbaijan State Economic University Az 1001 Baku Istiglaliayt Str.

Thermal conductivity as a function of temperature. Measured thermal conductivity λ eff of bulk insulation material marker as a function of temperature ϑ and model predictions lines. Thermal Conductivity of Graphite at High Temperatures where Ai Ri 1 2 ri 2 lnR i ri Ri 2 r i 22 i an index of a sample R i external radius ri- internal radius Т1 Т2 - true values of temperature on an internal surface of samples. It is usually assumed that the thermal conductivity is not a function of the temperature gradient but is a function of the state composition purity perfection physical structure and other.
THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY OF PEACH RASPBERRY CHERRY AND PLUM JUICES AS A FUNCTION OF TEMPERATURE AND CONCENTRATION MIKAIL A. Thermal Conductivity as a Function of Temperature and Relative Humidity Ilkka Valovirta Juha Vinha Member ASHRAE Ilkka Valovirta is a research scientist and Juha Vinha is a senior research scientist in the Depart ment of Civil Engineering Tampere University of Technology Tampere Finland. At higher temperatures thermal conductivity decreases in all the steels so the data converge.
For comparison purposes reference values are reported at an agreed temperature usually 298 K 25 C or 77F although occasionally 20 C 68Fis used. The lowest thermal conductivity could be measured for expanded perlite with about 005 Wm K at 20 C. The water content below which the apparent thermal conductivity is not affected by water content is a function of the soil.
The apparent thermal conductivity was independent of water content at very low water contents. At very low temperatures the thermal conductivity is proportional to temperature. Thermal conductivity is the fundamental property of material that gives a measure of effectivity of the material in transmitting heat through it.
In refractories thermal conductivity is a function temperature and typically the thermal conductivity is higher at elevated temperatures. In metals where the valence electrons easily m ove in and out of the conduction bands the number of charge carriers n is large. It is usually assumed that the thermal conductivity is not a function of the temperature gradient but is a function of the state composition purity perfection physical structure and other.
Right-click the Thermal Conductivity box to select FunctionThe Functions dialog box opens. Here T is the dependent variable in Heat Transfer module. In native mode you can define the thermal conductivity of a material as a function of temperature.
It shows different nature for different material with temperature. 31 Azerbaijan 2Institute of Physics of the. For metals thermal conductivity generally decreases with increase in.
Thermal conductivity is fit by a power law k 63728T 1242 at high temperature but some mismatch occurs over 500 to 1100 K. Thermal Conductivity BTU-inft 2 h F Wm 2 K Thermal conductivity is a measure of heat transferred across a specific medium. This chart gives the thermal conductivity of gases as a function of temperature.
Due to the data source being a sample from. -127E-9 T3809E-6 T2- 837E-3 T2272. Generally the conductivity of a solution increases with temperature as the mobility of the ions increases.
ABDULAGATOV4 and NAZIM D. The independent variable of the function is temperature. Resistivity in metals is ther efore more a function of the mobility of the electrons.
I am creating a. Many different forms were tried in an attempt to produce a better fit to all temperatures. A cursory examination of the data for temperature versus thermal conductivity shows that there is a greater variation in thermal conductivity at lower temperatures.
I am trying to include thermal conductivity as a function of temperature in my model but its giving me error inconsistent unitlet us say the function is. Qs εt h σ T. The value of the heat flux density qs is defined under the Stephan-Boltzmans law 3.
Typical values of D0 and are listed in table 1 along with the calculated resistivity at 100C. The water molecules are in layers only a few molecules thick.
Thermal Conductivity Of Iii V Semiconductors Electronics Cooling

Aluminum Thermal Conductivity As A Function Of Temperature Data From Download Scientific Diagram

Thermal Conductivity As A Function Of Temperature For Fully Dense Download Scientific Diagram

Thermal Conductivity Of Mosi 2 As A Function Of Temperature 11 Download Scientific Diagram

Calculated Phonon Thermal Conductivity As A Function Of Temperature For Download Scientific Diagram
Understanding Thermal Conductivity Advanced Thermal Solutions

Thermal Conductivity As A Function Of Temperature And Time For P Type Download Scientific Diagram

Thermal Conductivity As A Function Of Temperature Of The 60 Mpa Sample Download Scientific Diagram

Variation Of Total Thermal Conductivity As A Function Of Temperature Download Scientific Diagram
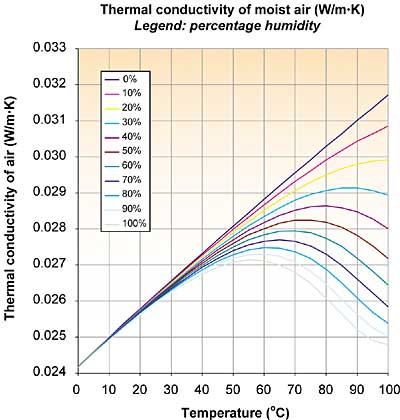
The Thermal Conductivity Of Moist Air Electronics Cooling

Thermal Conductivity As A Function Of Temperature Measured Along The Download Scientific Diagram

Thermal Conductivity As A Function Of Temperature For The Ceramics Download Scientific Diagram